Acne Types Facial Blemishes Treatments and Solutions
Acne Types Facial Blemishes Treatments and Solutions
Table of Contents
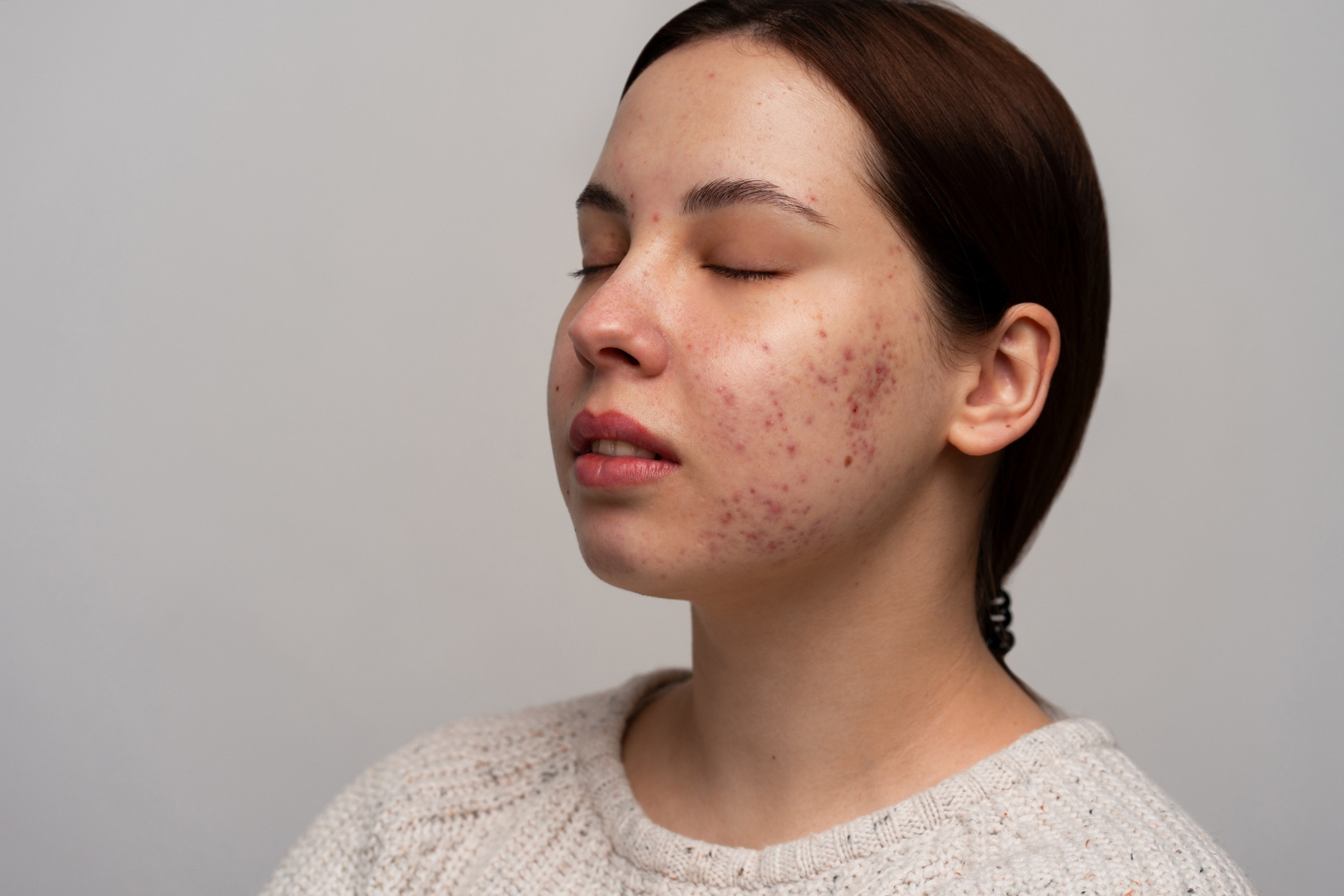
Facial blemishes those unwelcome spots bumps and imperfections can be a real source of frustration impacting self confidence at any age. While many simply say “acne” the truth is our skin can show a wide variety of concerns. To truly achieve a clearer healthier complexion the very first step is understanding exactly what type of acne or blemish you are facing. This comprehensive guide will explore the diverse forms of acne and other facial blemishes uncover their root causes and provide a detailed overview of treatment options covering everything from professional interventions to readily available over the counter and prescription products.
Demystifying the Terminology Acne Versus Blemishes:
Before we dive into specific types lets clarify some terms. “Acne” specifically refers to a skin condition involving clogged hair follicles leading to those familiar blackheads whiteheads pimples and even cysts. “Blemish” however is a much broader term encompassing any mark or imperfection on your skin. This includes acne lesions yes but also scars dark spots known as hyperpigmentation and other irregularities in your skins texture. While this article will primarily focus on the various forms of acne we will also touch on related blemishes that often appear alongside or as a result of acne.
The Root of the Problem Understanding Acne Causes:
Acne is a complex issue influenced by a network of interconnected factors:
- Excess Sebum Production: Our skins sebaceous glands produce sebum an oily substance that keeps our skin lubricated and protected. Hormonal shifts genetics and even certain medications can trigger these glands to produce too much sebum.
- Clogged Hair Follicles: When there is too much sebum it can mix with dead skin cells causing them to stick together and ultimately clog our hair follicles or pores.
- Bacteria Propionibacterium Acnes P Acnes: This bacteria naturally resides on our skin. However when hair follicles become blocked P acnes can multiply rapidly within the confined pore leading to inflammation.
- Inflammation: The combination of bacteria and blocked follicles sets off an inflammatory response within the skin. This results in the redness swelling and tenderness we associate with acne lesions.
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Changes in our hormone levels particularly during puberty menstruation pregnancy and times of stress can significantly impact sebum production and contribute to the development of acne.

Decoding the Different Faces of Acne:
Acne isnt a one size fits all condition. It appears in various forms each with its own distinct characteristics:
-
Non Inflammatory Acne: These types of acne typically dont involve significant redness or swelling.
- Blackheads Open Comedones: These appear as small dark spots right on the skins surface. The darkness isnt dirt but rather the oxidation of sebum and melanin our skins pigment when exposed to air.
- Whiteheads Closed Comedones: These are small flesh colored or whitish bumps with a closed pore. The sebum and dead skin cells are trapped beneath the skins surface.
-
Inflammatory Acne: These types of acne are marked by redness swelling and often tenderness or pain.
- Papules: These are small raised red bumps that are often tender to the touch. They dont contain pus.
- Pustules: Similar to papules but these contain pus appearing as red bumps with a white or yellow center. These are what many people commonly refer to as “pimples.”
- Nodules: These are large firm painful lumps that develop deep beneath the skins surface. They are a result of significant inflammation and can persist for weeks or even months.
- Cysts: These are also large painful pus filled lumps that form deep within the skin. They are often softer than nodules and can be prone to scarring. Cystic acne is considered a severe form of acne.
-
Other Specific Types of Acne:
- Fungal Acne Malassezia Folliculitis: Despite its name this condition is actually caused by an overgrowth of yeast Malassezia which naturally lives on our skin rather than bacteria. It often appears as small uniform itchy bumps commonly on the chest back and upper arms but can also affect the face.
- Hormonal Acne: This type of acne has a direct link to hormonal fluctuations often flaring up around menstruation during pregnancy or with hormonal therapies. It commonly appears on the lower face jawline and chin.
- Cystic Acne: As mentioned earlier this is a severe form of inflammatory acne characterized by numerous deep painful cysts and nodules. It often requires professional medical treatment.
Beyond Acne Common Facial Blemishes:
While acne is a primary concern our faces can also be affected by other blemishes:
- Acne Scars: These are permanent changes in the skins texture resulting from inflammation and damage during acne breakouts. They can be atrophic depressed or hypertrophic raised.
- Post Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation PIH: These are dark spots or patches that linger on the skin after an acne lesion has healed. They are caused by an overproduction of melanin during the inflammatory process.
- Rosacea: This chronic inflammatory skin condition causes redness flushing visible blood vessels and sometimes small red pus filled bumps. It is often mistaken for acne but has different underlying causes and treatments.
- Perioral Dermatitis: This condition presents as small red bumpy rashes around the mouth nose and sometimes eyes. Its exact cause is unknown but may be linked to topical steroid use or certain cosmetics.
The Treatment Toolkit Strategies for Clearer Skin:
Treating acne and facial blemishes requires a personalized approach tailored to the specific type and severity of the condition. Treatment options range from readily available over the counter OTC products to prescription medications and professional procedures.
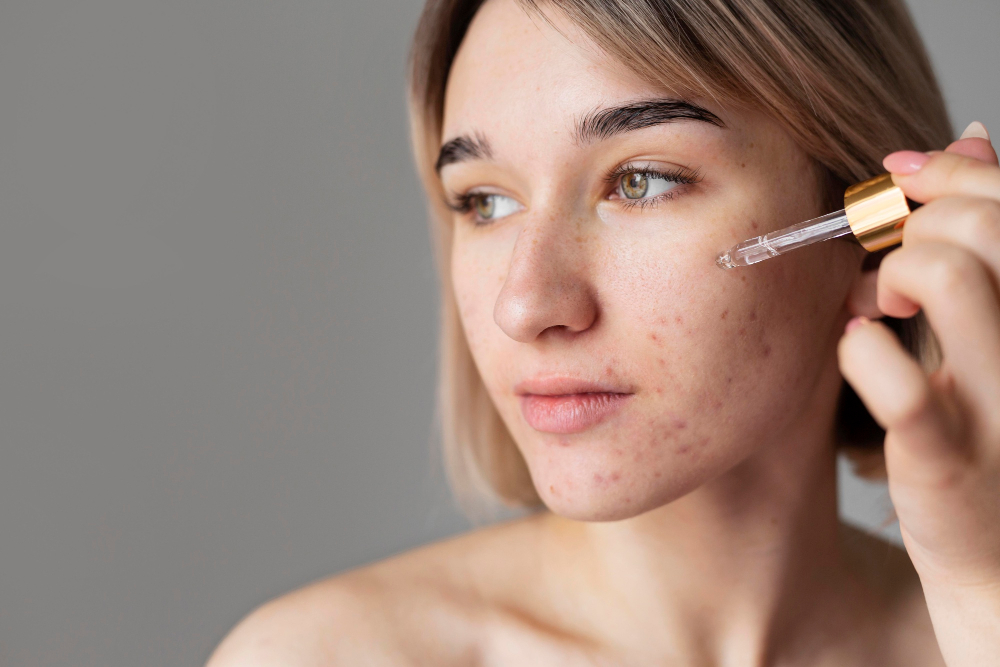
Over the Counter OTC Treatments:
These products can be purchased without a prescription and can be effective for mild to moderate acne:
- Benzoyl Peroxide: This antibacterial ingredient helps to kill P acnes bacteria and reduce inflammation. It comes in various strengths from 25% to 10% in cleansers creams and gels. Product Example: A benzoyl peroxide wash known for its effectiveness.
- Salicylic Acid: This beta hydroxy acid BHA helps to exfoliate the skin unclog pores and reduce inflammation. You can find it in cleansers toners and spot treatments. Product Example: A salicylic acid exfoliant popular for clearing pores.
- Adapalene: This topical retinoid previously prescription only is now available OTC in lower strengths 01%. It helps prevent clogged pores and reduce inflammation. Product Example: An OTC adapalene gel known for its gentle yet effective action.
- Azelaic Acid: This naturally occurring acid has both antibacterial and anti inflammatory properties and can also help fade hyperpigmentation. Its available in some OTC and prescription formulations. Product Example: An azelaic acid suspension praised for its multi action benefits.
Prescription Medications:
For moderate to severe acne or blemishes that dont respond to OTC options a dermatologist may prescribe stronger medications:
- Topical Retinoids: These prescription strength vitamin A derivatives such as tretinoin adapalene 03% and tazarotene help prevent clogged pores reduce inflammation and promote skin cell turnover.
- Topical Antibiotics: These including clindamycin and erythromycin help to kill P acnes bacteria and reduce inflammation. They are often used in combination with benzoyl peroxide to prevent antibiotic resistance.1
- Oral Antibiotics: These such as doxycycline and minocycline are used for moderate to severe inflammatory acne to reduce bacteria and inflammation throughout the body. They are typically prescribed for a limited duration.
- Hormonal Therapies: For women experiencing hormonal acne oral contraceptives or spironolactone an anti androgen medication can help regulate hormone levels and reduce breakouts.
- Isotretinoin: This powerful oral retinoid is reserved for severe nodular cystic acne that has not responded to other treatments. It significantly reduces sebum production inflammation and bacteria. It has potential side effects and requires careful monitoring by a dermatologist.
Professional Treatments:
Dermatologists offer a range of in office procedures to address acne and related blemishes:
- Chemical Peels: These involve applying a chemical solution to the skin to exfoliate the top layers helping to unclog pores reduce inflammation and improve skin texture and hyperpigmentation.
- Microdermabrasion: This mechanical exfoliation technique uses tiny crystals or a diamond tipped wand to remove the outermost layer of dead skin cells. It can be helpful for mild acne and blackheads.
- Laser and Light Therapies: Various light based treatments such as blue light therapy and pulsed dye laser can target P acnes bacteria reduce inflammation and improve the appearance of acne scars and hyperpigmentation.
- Corticosteroid Injections: Direct injections of anti inflammatory medication into large painful nodules or cysts can provide rapid relief.
- Acne Extraction: A dermatologist or trained aesthetician can safely remove blackheads and whiteheads using specialized instruments.
Targeting Specific Acne and Blemish Types:
- Fungal Acne: This is typically treated with antifungal shampoos used as a body wash or topical antifungal creams or oral antifungal medications prescribed by a dermatologist.
- Hormonal Acne: Treatment often involves hormonal therapies combined with topical treatments.
- Cystic Acne: This severe form usually requires a combination of oral isotretinoin oral antibiotics and sometimes corticosteroid injections.
- Acne Scars: Treatment options include topical retinoids chemical peels microdermabrasion laser resurfacing microneedling and dermal fillers.
- Post Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation PIH: Treatments include topical retinoids azelaic acid vitamin C serums niacinamide chemical peels and laser therapies.
- Rosacea: Treatment focuses on managing symptoms with topical medications such as metronidazole and azelaic acid oral antibiotics and laser or light therapies.
- Perioral Dermatitis: Treatment typically involves stopping the use of potential trigger products like topical steroids and using topical or oral antibiotics.
Building Your Skincare Routine for Clearer Skin:
A consistent and gentle skincare routine is fundamental for managing acne and preventing future breakouts:
- Cleanse: Use a gentle non comedogenic cleanser twice daily to effectively remove dirt oil and makeup. Product Example: A gentle foaming cleanser suitable for daily use.
- Treat: Apply targeted treatments containing active ingredients such as salicylic acid benzoyl peroxide or adapalene following the product instructions.
- Moisturize: Even oily skin needs a lightweight non comedogenic moisturizer to maintain proper hydration levels and prevent the skin from overproducing oil. Product Example: A lightweight hydrating gel moisturizer.
- Protect: Apply a broad spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher every morning to shield your skin from sun damage which can worsen both acne and hyperpigmentation. Product Example: A non greasy broad spectrum sunscreen.
Lifestyle Factors and Acne:
While a solid skincare routine is key certain lifestyle factors can also influence acne:
- Diet: While the direct link between diet and acne is still being researched some studies suggest that high glycemic foods and dairy might trigger breakouts in certain individuals.
- Stress: Stress can lead to hormonal shifts that can exacerbate acne. Incorporating stress management techniques may be beneficial.
- Sleep: Getting adequate sleep is important for overall skin health and can indirectly impact acne.
- Avoid Picking and Squeezing: Manipulating blemishes can significantly worsen inflammation increase the risk of scarring and introduce infection.
When to Seek Professional Guidance:
Its recommended to consult a dermatologist if you experience:
- Severe acne characterized by nodules and cysts.
- Acne that shows no improvement with over the counter treatments.
- Acne that is causing noticeable scarring or significant emotional distress.
- Any signs of infection such as increased redness pain swelling or pus.
- Uncertainty about the specific type of acne or blemish you have.
Conclusion:
Understanding the various types of acne and facial blemishes along with the available treatment options empowers you to take proactive steps towards achieving clearer healthier skin. By accurately identifying your specific skin concerns establishing a consistent and appropriate skincare regimen and seeking professional guidance when necessary you can embark on a successful journey to a more confident complexion. Remember that patience and consistency are vital and with the right approach clearer skin is absolutely attainable.











